Windows 2.0
| Windows 2.0 | |
|---|---|
| Part of the Microsoft Windows family | |
 |
|
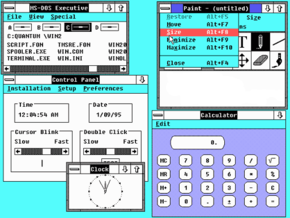
| Screenshot of Windows 2.0 | |
| Developer | |
| Microsoft | |
| Website | http://www.microsoft.com/ |
| Releases | |
| Release date | November 1987 (info) |
| Current version | 2.03 (November 1987) (info) |
| Source model | Closed source |
| License | MS-EULA |
| Support status | |
| Unsupported as of 31 December 2001 | |
Windows 2.0 is a 16-bit Microsoft Windows graphical user interface-based operating environment that was released in November 1987 and superseded Windows 1.0. With Windows 2.1x in 1988, Windows 2.0 was supplemented by Windows/286 and Windows/386. Windows 2.0, Windows/286 and Windows/386 were superseded by Windows 3.0 in May 1990, but supported by Microsoft for fourteen years, until 31 December 2001.
Contents |
History
Application support
The first Windows versions of Microsoft Word and Microsoft Excel ran on Windows 2.0. Third-party developer support for Windows increased substantially with this version (some shipped the Windows Runtime software with their applications, for customers who had not purchased the full version of Windows). However, most developers still maintained DOS versions of their applications, as Windows users were still a distinct minority of their market.
Applications shipping with Windows 2.0:
- CALC.EXE
- CALENDAR.EXE
- CARDFILE.EXE
- CLIPBRD.EXE
- CLOCK.EXE
- CONTROL.EXE
- CVTPAINT.EXE
- MSDOS.EXE
- MSDOSD.EXE
- NOTEPAD.EXE
- PAINT.EXE
- REVERSI.EXE
- TERMINAL.EXE
- WRITE.EXE
Legal conflict with Apple
On 17 March 1988, Apple filed suit against Microsoft and Hewlett-Packard, accusing them of violating copyrights Apple held on the Macintosh System Software[1]. Apple claimed the "look and feel" of the Macintosh operating system, taken as a whole, was protected by copyright and that Windows 2.0 violated this copyright by having the same icons.
Features
Windows 2.0 allowed application windows to overlap each other unlike its predecessor Windows 1.0, which could display only tiled windows. Windows 2.0 also introduced more sophisticated keyboard-shortcuts and the terminology of "Minimize" and "Maximize", as opposed to "Iconize" and "Zoom" in Windows 1.0.
References
- ↑ "1980 - 1989: An Industrial Milestone". The Apple Museum. http://www.theapplemuseum.com/index.php?id=56. Retrieved 4 September 2009.
External links
- GUIdebook: Windows 2.0 Gallery – A website dedicated to preserving and showcasing Graphical User Interfaces
- ComputerHope.com: Microsoft Windows history
- Microsoft article with details about the different versions of Windows
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||